Building a house in Malaysia? See sample house plans or contact me to design a new house for you!
Chapters:
statistics
housing types
villages
building code
crazy stuff
about
Some westerns wrongly see Malaysia as a third-world country. Malaysia is a fast-growing economy population doubled in last 25 years due to immigration. Like Singapore, Malaysia evolved from villages (kampung) into modern landed housing and high-rise condominiums. If in Eastern Europe most of housing dates back from communist times (<1990), Malaysia construction industry is booming and most houses are recently built.
Looking at GDP per Capita, we can see that Malaysia developed rapidly during 1980s and 1990s. 1997 Asian Crisis plunged economy down, time in which Eastern European countries were evolving rapidly. Currently Malaysia is a middle-income country similar with countries in Eastern Europe, but having much lower cost of living.
The government subsidy many things including gas (I am not sure if this is good, cheap gas encourage travel with personal cars rather than public transport, cause urban sprawl, traffic jams and pollution). Update: this lower cost of workforce and may encourage foreign investment.
Petronas Towers (452 meters tall) was the world tallest building between 1998 and 2004. Merdeka 118 (680 meters tall) became the second-tallest building in the world in 2023.
At this moment I do not know many details about living conditions, how good is education, healthcare, crime, etc. Maybe some locals can help me with an “internal opinion”?
Malaysia housing statistics
Malaysia have a total of 7,346,910 housing units, of which Detached 2,416,210, Semi-detached 528,408, Terrace/link 2,570,317, Townhouse 32,682, Cluster 63,345, Flat 744,187, Apartment or condominium 716,729, few more housing types do exist (as 2010). Home ownership ratio 72.5%. Source: krinstitute.org.
Malaysia housing types
Housing in Malaysia is similar in style and types with Singapore housing, but cheaper and bigger houses and apartments, due to lower land prices and lower salaries.
The equatorial climate (absence of heating systems) and the lifestyle with big families, turned Malaysia into a country with one of the biggest houses in the world. Average household size dropped from 4.62 in 2000 to 4.31 in 2010 (source: census report, page 31 and statistics.gov.my), I am in doubt if this was caused by influx of foreigners with different lifestyle, or due to increased wealth of Malay families and married kids moving away from parent’s house?
Most houses and apartments in Malaysia have 3 or more bedrooms. Searching on Google for 2-bedroom or studio apartments I do not see many results.
Flats (public housing apartments) can be small as 60 sqm and still have 3 bedrooms! Example floor plan Pangsapuri Seri Nilam.
Apartments and Condominiums (privately built) have usually 3 bedrooms, around 100-120 sqm, but there are also examples over 400 sqm and 5 bedrooms.
Terraced House are most common type of home for Malaysians. Most new terraced houses are 2-storey and have 4 bedrooms, usually 6000 mm or 6700 mm wide (approximate metric values of 20 and 22 feet), and 12-14 meters depth, and about 150-200 sqm if they are 2-storey, up to 300 sqm in case of 3-storey terraced houses. Single-storey terraced houses are around 100 sqm with 3 or 4 bedrooms, some bedrooms being windowless. I have not seen yet any house with less than 3 bedrooms. Would like to know what is average family size in these oversized houses.
Semi-detached house are shared by 2 families living side by side.
Bungalow (detached house) are a symbol of luxury inside cities, they have usually 4, 5, or even 6 bedrooms, each with own bathroom, some are 3-storey, reaching over 400 sqm. But detached houses in rural areas are also called bungalow, most of them being single-storey, dragging down average house size.
Townhouse is a building shared by 2 families living one above other, both having entrances on ground floor, usually 2-storey and 3 bedrooms, but one day I saw a 4-storey townhouse on sloped ground, where one family had entrance at 1st level while second family had entrance at 3rd level from opposite side. I lost URL so if anyone know where it is located please tell.
Link house is a term which include terraced houses and townhouses which are build like terraced (townhouses can be semi-detached too).
Superlink house is a term that I do not know the original meaning, but today most link houses are called superlink for marketing purposes.
There is also new interesting housing styles, quaduplex, sextuplex, honeycomb (example).
A large part of housing stock remains the old houses built 1960s to 1980s when Malaysia was just a third-world country, these old houses looks quite ugly and not properly maintained, but still better than houses of same age from other Asian countries.
Minimum ceiling height is 2.5 m but most houses are built in 2.5-3 m range, some high-end bungalow may have even 4 m ceiling (personal estimation from photos, anyone who is living or have been in Malaysia please provide more accurate data).
Update: Google Streetview in Malaysia launched on 26 September 2014, allowing me to see that this country is worse than I expected, many houses are single-storey, further study is required when I have free time, for more precise estimation of house sizes!
Luxury apartments from Putrajaya and Mont Kiara
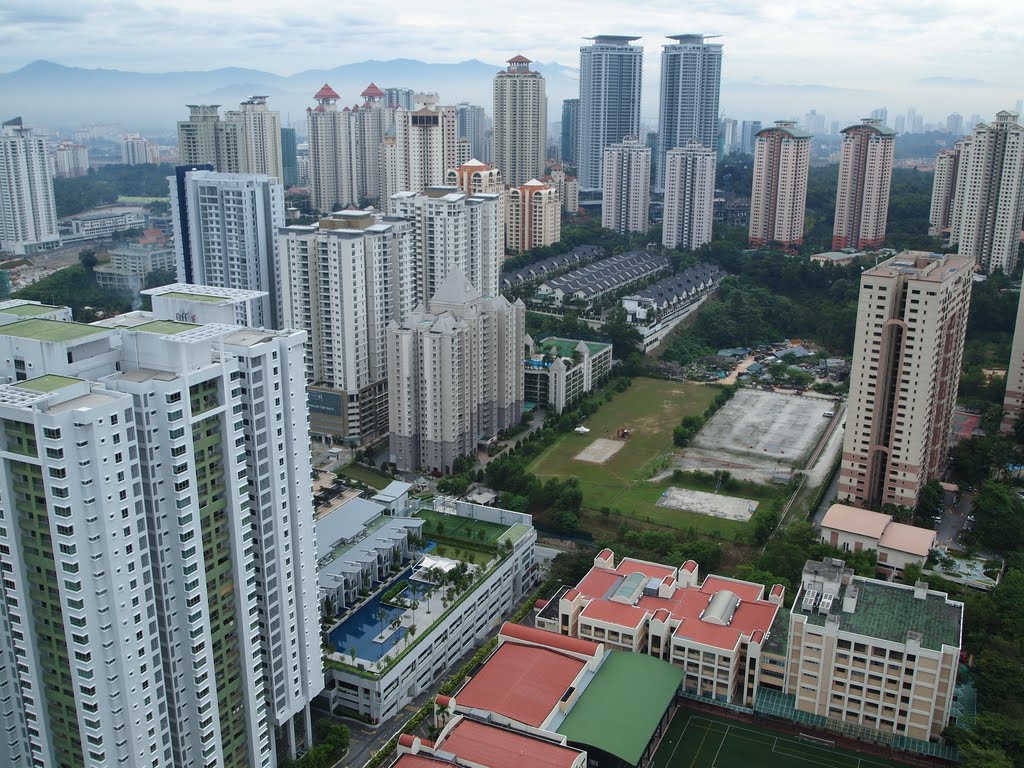


More photos of luxury condominiums around Mount Kiara on https://mapio.net/wiki/Q5522260-en/ (dead website)
Low-cost apartments (public housing)
Malaysia kampung
Another beautiful part of Malaysia is the countryside… the kampongs. Houses with big garden, a lot of greenery and no fence, contrasting the concrete jungle of cities. Traditional Malay houses were made by bamboo or timber, built on stilts to protect from flood and wild animals, and for better ventilation. Windows are louvre type, again for ventilation.
Kampung houses are smaller than the houses in the cities, but still big considering the poverty of people living there.
Small towns, like the following video, have a mix of kampung-styled houses and modern houses.
Malaysia also have slums, houses built over water, probably with little or no running water or proper sanitation, but even they are large, around 50-100 sqm, not like the 5-10 sqm slums of India or Philippines.
Malaysia building code
Download building code: Uniform Building by Laws.
Malaysia building code specify minimum 10 feet / 3.05 meters setback from side and rear property line, and 20 feet / 6.10 meters from street, also 10 feet / 3.05 meters of carport roof. corner lots usually have large courtyard 6 meters wide in side of house.
However, most houses are built with longer setbacks around 9 meters from street, thus you can park 2 small cars one behind other. Does anyone know when the current building code was issued and what were the earlier laws about setback?
Google satellite imagery and street view shows numerous houses expanded, carport lengthened to the street line, etc. How these building code violations were possible? Corrupt authorities?
Crazy stuff found during my study of housing in Malaysia
Crazy urban planning: if in United States there are 1/2-storey houses mixed with 3-storey apartments, and in Europe there are 2-storey houses mixed with 4-storey apartments, in Malaysia there are 20-storey blocks built in middle of a 2/3-storey landed housing development! How does this explain?
Bad apartment layout: in a country dominated by low-density developments, many condominiums, despite of large open space in their compounds, the apartment towers are massive, with large number of units per floor. Thus the apartment layouts are bad and crammed, some blocks being 30 meters wide with double-loaded corridors, 3 bedroom apartments of which only living room and master bedroom have view to outside, the other 2 bedrooms are facing inside of block towards the corridor, ventilated through a small airwell.
4 bedrooms is a STANDARD in Malaysia even for single-storey terraced houses! Example: Austin Residence, but… 2 bedrooms are windowless! Is this legal in Malaysia!!?? Someone has told me that is legal if they have high-level windows, over the ceiling of nearby room. However the picture does not show this.
3 bedroom can be found nowadays only in townhouses (2 families sharing same house)
A very old back to back terrace house with 2 bedrooms. Fortunately there are not many such shitty houses: //www.iproperty.com.my/propertylisting/2661616/seberang-jaya-2-sty-terrace-link-house-forsale (link dead)
The ONLY house with 2 bedrooms found so far: //bestmalaysiaproperty.com/house/show/?h=09d37c08f7b129e96277388757530c72 (link dead)
Mutiara Seputeh, a development with 93 houses ranging from 400-870 sqm (floorplans available).
Some luxury apartments reach 400 sqm as well.
Further read:
Housing Statistics 2015
Malaysia Housing Policcy (PDF)
Case study of the low-cost public housing in Malaysia.
Malaysia is located in the most raining region of earth, so… best to avoid buying houses near rivers. Worst affected was Kota Tinggi in 2006-2007.


See 100+ flood photos on yazidtim‘s Panoramio account.
STUDY TO BE CONTINUED… but I don’t know what else to write here.
Oh… don’t forget, somebody should tell to Johor Bahru to expand the city further away from coast and stop deforesting the areas around Singapore. From where Singapore will get fresh air when it will be fully urbanized?
About
Page published for first time in 2011 and updated over next years with more information found by me or provided by visitors. Text written by me (Teoalida) and images taken from Wikipedia, Panoramio and other websites. Do you have useful information that worth adding? Did you found an error or have a contradictory opinion? Leave a comment!








Stumbled upon this blog. Very interesting. You can get most of the information on the share of landed and high-rise living quarters from the Department of Statistics.
Some information are correct while some are merely based on judgement. The building codes allow any landed house to be renovated, subject to approval from local authorities. Not sure about corrupt authorities, which I think there might be very few cases happened. In general, as long as Malaysians have the land to ‘expand the house’ (unlike Singapore which has limited land), the authority will allow the renovation as long as it is within the limit. But there are cases where the house owner will renovate the house first without approval, which in return they will be fined (and demolished if considered obstructing public spaces) by the authorities.
It is quite interesting that the way how the blog was written is merely on judgement and of course lots to do with generalising and cherry picking. I would like to suggest for you to look at both sides – the best and the worse so that it won’t make bias conclusion.
I’m not sure Johor Bahru wants to stop the development at the coastal area. It’s their land which they can do whatever they want. Johor has enough forest for them anyway. Oh.. don’t forget, somebody should tell Singaporean that they can buy houses in Johor if fresh air is what they really want.
Couldn’t you provided link to which page of department of statistics show share of landed houses?
I always look at both sides, best and worst of each country, but in case of Malaysia I don’t see much worst. Can you tell me more bad things from Malaysia? See what I write about https://www.teoalida.com/world/india/ and https://www.teoalida.com/world/philippines/
I know at least 1 person who is living in Johor and commuting daily to Singapore to work. Maybe more people will do this if customs will work faster.
its a regulation to have minimum of 3 bedrooms here in Malaysia, because we applied Islamic approach, where parents rooms have to be separated from boys and girls. that is the minimum consideration
I hardly believe this, been contacted by numerous people from countries with stronger Islamic religion from Middle East and some of them build fewer bedrooms and avoid bathrooms to be attached to bedrooms. Also how about old couples.which children grown up and moved away? Do they also need to buy a 3 bedroom house?
I think the previous explanation is misleading. There is no laws that stated the requirements of having 3 bedrooms (even more relate it with Islamic approach). Most of the design is based on market survey- for example , Malay race normally prefer 4 bedrooms as the have big families and tend to have mixed generations staying together. Hence it’s explain why most of the development is having 3-4 bedrooms because of the market demand (the highest population in Malaysia is Malay race).
Other than that, by having bigger built up area, the developer can make more money.
For the window requirement – yes, the authority has imposed that every habitable room need to fulfill xx% of natural lighting and ventilation (it’s stated in Malaysia Uniform Building By Law).
Does price per square meter in Malaysia is higher for small or big houses? In Singapore in 1990s big apartments had higher price per square meter but after the 1990s bubble things got reversed and now developers build small flats, “shoebox” 35-50 sqm because they can make more money this way.
My parent’s house is a semi-detached house sharing with a neighbour. He sold the house and the new owner decided to demolish the house to build a much bigger house leaving my parent’s house looking really weird. They built it to the maximum land space leaving no land for garden. As their house is a corner lot, it looks even weirder. When they demolished their house, they caused leakage in my parent’s house especially when it rains. Is there any law against this?
Cam anyone advice me on this?
This happen often in Singapore too, lots of semi-detached houses being rebuilt independently but setback rules should be followed. Regarding lacking, you should ask your neighborhood to pay your repairs, if he refuses I don’t know what is the legal way to solve such dispute.
Do you have any data on Average Home size (in square meters) of the newly built homes or a source from where I can find it? I tried department of Statistics but without any luck. Also, any clue as to what is the typical electricity consumption per year?
Great insights by the way. Thanks for sharing!
Indeed Malaysia government don’t track statistics of average house size. We can only estimate an average from floor plans provided by developers, around 100-200 sqm.
do you know how much the high end housing is ? also the prices for the low end housing? I’ve been trying find out for a while now.
Prices vary significantly between Kuala Lumpur and villages in Sabah and Sarawak, also there is no clear definition of low / high end housing, to include an exact price in article, but you can browse http://www.iproperty.com.my and http://www.propertyguru.com.my and other similar websites, and judge yourself.
do you know the standard of the floor area per person?or the size of house per people?
There is no standard, and government do not provide statistics about house sizes, they only provide average household size 4.62 in 2000 and 4.31 in 2010. Do note that Malaysia have high income inequality so there may be families of 10 people living in a 60 sqm public housing flat as well as families of 5 living in a 1000 sqm luxury bungalow.
May i know where u get the info of types of house in malaysia ?
I have been doing a bit of research on building code as I am interested in building my own house. Drawing my floor plans. I have seen some images where the setback for terrace corner lots on the side (not front) facing the street must be 20 ft. Is this also true for detached housing?
Also currently wondering if it’s feasible to implement something that can survive on grid-down scenarios (no grid power/water) maybe even try to grow some food. I know well water is possible in some areas, but unsure about whether solar+battery is feasible in Malaysia.
Apartment development in tourist sector is very interesting. For example Genting Highlands with Amber Court and many new stuff built around it
I’m from Malaysia and I also look at house realtor websites on other countries as well as Google Street Map coverage of other countries. I find that Malaysian buildings are much uglier compared to that in Western countries. The normal roads are also not paved as well. Also, I would hardly call those areas “luxury”. Sure these terraces have pedestrian paths and decorative trees on the road side but most if not all streets in the West have them including low cost areas, and even the low cost areas over there reflect greater workmanship in that. As for the flats they look so tacky. If you ask me, our government need to set up an architectural department ASAP and fix most of the buildings that are in Malaysia
Depending by what do you mean with “Western countries”
India and Middle East is west compared with Malaysia and are by far worse than Malaysia, roads much narrower and without trees between road and sidewalk, in India you also see dense slums and trash everywhere. Japan also have dense houses and roads narrow as 4 meters in residential areas, but they are clean.
But if you compare with Western Europe or United States, indeed Malaysia houses are uglier. Remember than Malaysia was a third-world country in 1980, I also notice poor maintenance of old houses. Malaysian. houses built 20 years ago looks worse than houses built 100 years ago in Europe and USA.
The SIZE of Malaysia houses give me impression of luxury, I don’t know if any other country of Asia have bigger houses. We need to talk more about this.
39. Natural lighting and ventilation.
(1) Every room designed, adapted or used for residential, business or other purposes except hospitals
and schools shall be provided with natural lighting and natural ventilation by means of one or more
windows having a total area of not less than 10% of the clear floor area of such room and shall have
openings capable of allowing a free uninterrupted passage of air of not less than 5% of such floor
area.
42. Minimum areas of rooms in residential buildings.
(1) The area of the first habitable room in a residential building shall be not less than 11 square
metres, the second habitable room be not less than 9.3 square metres and all other rooms be not less
than 6.5 square metres in area.
(2) The width of every habitable room in a residential building shall be not less than 2 metres.
(3) The area and width of a kitchen in a residential building shall be not less than 4.5 square metres
and 1.5 metres respectively
44. Height if rooms in residential buildings, shophouses, schools, etc.
(1) The height of rooms in residential buildings other than shophouses shall be–
(a) for living rooms and bedrooms, not less than 2.5 metres;
(b) for kitchens, not less than 2.25 metres;
(c) for bathrooms, water-closets, latrines, porches, balconies, verandahs, garages and like,
not less than 2 metres
(2) The average height of rooms with sloping ceilings in residential buildings other than shophouses
shall be–
(a) for living rooms and bedrooms, not less than 2.5 metres;
(b) for kitchens, not less than 2.25 metres;
(c) for bathrooms, water-closets, latrines, porches, balconies, verandahs, garages and the
like, not less than 2 metres.
Provided that not part of any room shall be less than 2 metres in height.
Source: Uniform Building By-Laws 1984
Danke für die tollen Berichte und Fotos. Das hat mir sehr viele Freude bereitet, “dabei” zu sein.
URL: urlaub-familienbett-allgäu.de (dead website)
“Google satellite imagery and street view shows numerous houses expanded, carport lengthened to the street line, etc. How these building code violations were possible? Corrupt authorities?”
Those are illegal extensions, but Malaysian politics of public governance is extremely populist. Corruption is part of it, but if you’re an authority personnel trying to go authoritarian on these ‘people stuff’, you will see the backlash from the general public painting the authority as oppressive, doesn’t matter if the imposition is just and lawful or otherwise.
Basically the general public don’t understand the requirements of modern civilization and development.